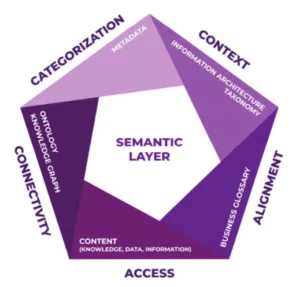
What is a Semantic Layer?
A semantic layer is a translation bridge between complex raw data and business users. It simplifies access to data by converting technical database structures into familiar business terms, making it easier for non-technical users to explore, analyze, and generate insights without deep knowledge of coding or database architecture. In other words A semantic layer is a business-friendly, virtual layer on top of raw data that translates complex database structures into familiar business terms.
Think of it as a translator: it maps technical data (tables, joins, keys) into concepts like “Revenue,” “Customer,” or “Churn Rate” — so analysts and business users can query data without needing to understand SQL or the underlying schema.
Key Benefits of a Semantic Layer
A well-designed semantic layer offers several advantages that enhance data accessibility, consistency, and security:
-
Consistency
Centralizes business logic (e.g., KPIs, metrics), so everyone uses the same definitions across dashboards, tools, and reports. Actually, All teams work with unified definitions, reducing discrepancies in reporting and decision-making. -
Empowers Self-Service Analytics
Empowers non-technical users to explore data using tools like Looker, Tableau, or Power BI without writing SQL. Enables employees to explore and visualize data without IT intervention. -
Simplifies Data Access Business users can query data using familiar terms instead of complex SQL queries.
-
Decoupling Logic from Data Storage
Business logic lives in the semantic layer, not buried in dashboard tools or code — making it easier to update and audit. - Improves Performance – Optimizes query execution for faster and more efficient data retrieval.
-
Data Governance & Security
Access controls and row-level security can be enforced directly in the layer, standardizing governance. - Enhances Security – Controls access, ensuring sensitive data is visible only to authorized users.
Modern Applications of the Semantic Layer
Semantic layers play a crucial role in various industries and technologies:
- Data Virtualization – Integrates multiple sources without duplicating data, creating a unified view of information.
-
dbt Semantic Layer: Allows you to define metrics directly in your dbt project and expose them to BI tools.
-
LookML (Looker): Google’s semantic modeling language to define metrics, dimensions, and explore structures.
-
Cube.js / Transform / MetricFlow: Open-source and SaaS tools that create semantic layers for modern data stacks.
-
Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms – Tools like Power BI and Tableau rely on semantic layers to deliver intuitive insights. It can connect to semantic layers to access clean, curated datasets.
- Cloud Data Warehouses – Helps companies optimize analytics across platforms like Snowflake, BigQuery, and AWS Redshift.
-
AI & Machine Learning – Enhances model accuracy by providing structured, contextually relevant data.
Why Your Business Needs a Semantic Layer
In today’s data-driven world, organizations must extract actionable insights quickly and efficiently. A semantic layer reduces complexity, ensuring stakeholders across different departments access accurate, reliable, and structured data without technical bottlenecks. Whether for marketing analytics, financial forecasting, or operational efficiency, adopting a semantic layer streamlines data workflows and enhances business intelligence.
Sample Semantic Layer Use Cases
The use of a semantic layer has the power to benefit companies across industries, as organizations strive to become truly data-driven:
- Retail: We’re far past the days of strictly brick-and-mortar sales. Retailers are collecting, processing, and analyzing more data than ever thanks to the expansion of eCommerce. A universal semantic layer helps these businesses consolidate their data from disparate sources – like POS systems, customer service touch points, and online stores – to make data-driven campaigns that increase conversions and meet consumer expectations.
- Healthcare: The pandemic made it clear that all industries, even those with strict privacy regulations like healthcare, need robust digital data literacy. A semantic layer can help analysts predict when and where ailments might happen, and who will be affected by them. That helps providers know where to allocate their time and resources, improving overall patient care.
- Financial Services: In a highly regulated industry like financial services, it can be tough for businesses to see their big picture all at once. Disparate resources, restricted access, and legacy systems make it hard to access all the necessary data. Semantic layers help aggregate and contextualize this siloed data so financial services leaders can make decisions with confidence and accuracy.
Final Thoughts
Implementing a semantic layer transforms how organizations interact with data. It bridges the gap between technical teams and business users, fostering better decision-making, efficiency, and innovation. If you’re looking to improve your organization’s data strategy, investing in a semantic layer is a powerful step toward a more data-literate future.
In short:
A semantic layer bridges the gap between raw data and business users, enabling trusted, governed, and consistent analytics — without reinventing business logic in every report.